If a single line in robots.txt could quietly tank your traffic overnight, would you catch it before it hurts revenue? That’s the hidden power and risk behind technical SEO. Understanding what is technical seo isn’t optional anymore. In 2025, it’s the difference between a site that wins visibility and one that’s invisible to customers.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- What is technical seo and how it powers crawling, rendering, and indexing
- Why it matters more than ever in 2025
- A complete technical SEO audit blueprint you can run in-house
- How to improve Core Web Vitals (LCP, CLS, INP) with practical fixes
- Canonicals, robots, noindex, hreflang, JavaScript SEO, structured data
- How to manage crawl budget, site speed, and internal linking for scalable growth
- Tools, checklists, and FAQs to keep you sharp
Want expert help implementing this? Get a tailored technical SEO audit at Ghodkes: https://ghodkes.com/
What Is Technical SEO? The Plain-English Answer
When people ask what is technical seo, here’s the simplest answer: it’s the foundation that helps search engines find, render, understand, and index your content fast and accurately. If on-page SEO tells your story and off-page SEO earns trust, technical SEO is the plumbing and wiring that keeps the whole house running.
Core areas include:
- Crawlability and indexability
- Site speed and Core Web Vitals
- Site architecture and internal linking
- Canonicalization and duplicate control
- Structured data and rich results
- JavaScript SEO and rendering
- Mobile-first indexing and responsive UX
- Security (HTTPS), redirects, and status codes
- Internationalization with hreflang
- Clean sitemaps and robots directives
Mastering what is technical seo gives your content a fair shot at ranking and converting.
Why Technical SEO Matters in 2025
Search has evolved. So have technical requirements. Here’s why it matters now:
- Mobile-first reality: Google primarily indexes your mobile version. Slow, clunky mobile pages lose visibility and revenue.
- Page experience expectations: Core Web Vitals (LCP, CLS, INP) shifted from “nice-to-have” to baseline. Better vitals correlate with stronger engagement and conversions.
- Complex websites: JavaScript frameworks, faceted navigation, and localization introduce rendering and duplication challenges.
- Quality and trust: Search Essentials emphasize accessibility, safety (HTTPS), and clear, indexable content. Technical missteps hide great content from search.
If you’re still wondering what is technical seo in practical terms, think of it as de-risking growth and unlocking performance already trapped in your site.
References:
- Google Search Essentials: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/fundamentals/search-essentials
- SEO Starter Guide: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/fundamentals/seo-starter-guide
How Search Engines Work: Crawl → Render → Index
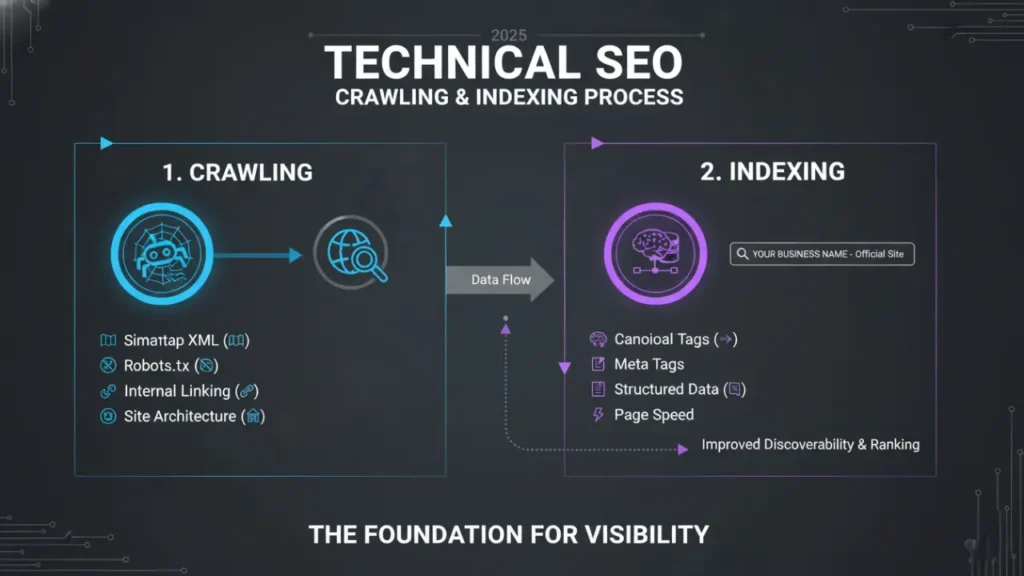

To really understand what is technical seo, follow the journey of a URL.
- Discovery and Crawling
- Bots discover URLs via links, sitemaps, and prior crawls.
- robots.txt rules govern where bots can crawl: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/robots/intro
- Rendering
- Search engines fetch HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, then render the page. Heavy, blocked, or delayed scripts can delay understanding of your content: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/javascript
- Indexing
- Parsed content, structured data, canonical signals, and directives determine what gets indexed and how it’s grouped with duplicates: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/overview-google-indexing
Technical SEO ensures each step is smooth, fast, and unambiguous.
The 2025 Technical SEO Audit Blueprint
Run this audit quarterly or after any major site change. It’s the practical backbone of what is technical seo in action.
1. Baseline and Goals
- Pull organic KPIs (sessions, impressions, clicks, conversions, revenue).
- Confirm analytics and conversion tracking are accurate.
- List priority templates (home, category, product/service, blog, location).
2. Crawl the Site
- Use a crawler (e.g., Screaming Frog, Sitebulb) to map URLs, status codes, titles, canonicals, directives.
- Flag 4xx and 5xx errors, redirect chains, duplicate titles/meta, thin pages, orphaned pages.
3. Index Status and Coverage
- In Google Search Console (GSC), review Indexing → Pages.
- Identify “Crawled – currently not indexed,” “Alternate page with proper canonical,” “Discovered – currently not indexed.”
- Prioritize fixes by revenue or importance.
4. Robots and Directives
- Confirm robots.txt isn’t blocking important sections.
- Sample robots.txt:
text
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Allow: /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
- Check meta robots and x-robots-tag usage (noindex, nofollow) on thin/utility pages.
5. Sitemaps
- Submit clean XML sitemaps with only indexable 200 URLs.
- Split large sites by type (e.g., /sitemap-products.xml, /sitemap-blog.xml).
- Docs: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/sitemaps/overview
6. Canonicalization and Duplicates
- Ensure one canonical URL per content piece. Avoid mixed signals (e.g., canonical to URL A but internal links point to URL B).
- Canonical tag example:
text
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com/preferred-url/” />
- Consolidate tags/filters/UTM duplicates. Use trailing slash and HTTP/HTTPS consistency.
7. Core Web Vitals and Performance
- Measure LCP, CLS, INP with PageSpeed Insights and field data: https://pagespeed.web.dev/
- Fix heavy images, render-blocking resources, layout shifts, and slow interactions (detailed section below).
8. Internal Linking and Architecture
- Keep important pages within 3 clicks of the homepage.
- Add contextual links to pass authority and help discovery.
- Use breadcrumbs and logical taxonomy.
9. Structured Data
- Implement JSON-LD for key templates (Article, Product, Organization, FAQ).
- Validate with Rich Results Test: https://search.google.com/test/rich-results
10. JavaScript SEO
- Ensure primary content is in the initial HTML where possible.
- Defer non-critical JS; avoid blocking resources; consider server-side rendering or pre-rendering if needed.
11. Internationalization (if applicable)
- Use hreflang for regional/language variants; confirm reciprocal, self-referencing tags.
- Docs: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/specialty/international/localized-versions
12. Security, HTTPS, and Status Codes
- Force HTTPS with HSTS; fix mixed content.
- Clean redirect chains; use 301 for permanent moves.
- Status code guide: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Status
13. Log File Analysis
- Review logs to see how often bots crawl important vs. wasted URLs.
- Trim crawl waste: filters, internal search, staging remnants.
14. Reporting and Roadmap
- Prioritize by impact: Indexing > Speed > Duplication > Internal links > Rich results.
- Track fixes and outcomes in GSC and analytics.
If you want a vetted process tailored to your stack, we’re happy to help at https://ghodkes.com/.
Core Web Vitals in 2025: LCP, CLS, INP
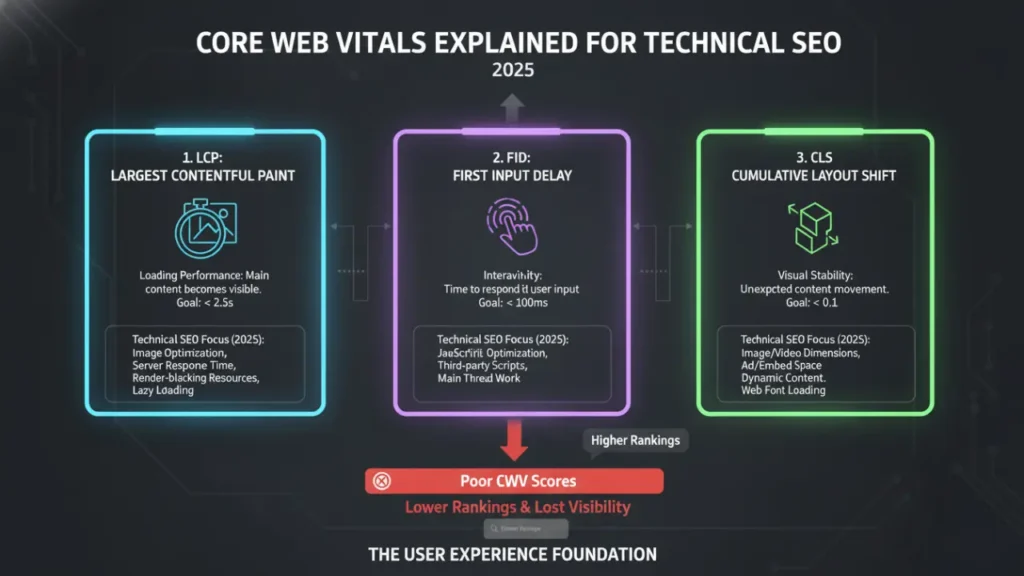

You can’t answer what is technical seo in 2025 without covering performance metrics that impact user experience and conversions.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Aim ≤ 2.5s. Optimize hero images, server response, and resource loading.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Aim ≤ 0.1. Reserve space for images/ads, avoid late-loading fonts, stabilize components.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Aim ≤ 200 ms. Reduce JS main-thread work, optimize event handlers, limit third-party scripts.
Practical fixes:
- Images: Use modern formats (WebP/AVIF), proper dimensions, lazy-load below the fold, preconnect/preload critical assets.
- CSS/JS: Minify, compress, remove unused CSS, split bundles, defer non-critical scripts, load fonts with font-display: swap.
- Server: Enable HTTP/2 or HTTP/3, use a CDN, implement caching (Cache-Control), compress with Brotli, optimize TTFB.
- Database: Query caching, indexes, and connection pooling for dynamic pages.
Helpful resources:
- Core Web Vitals: https://web.dev/vitals/
- INP details: https://web.dev/articles/inp
Site Architecture and Internal Linking
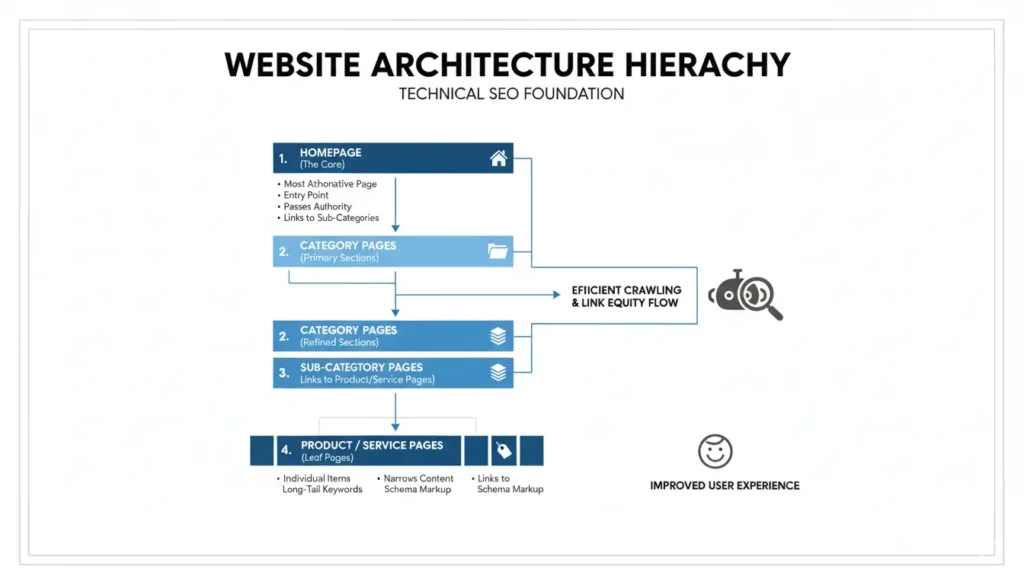

Technical SEO thrives on clarity. If you’re still wondering what is technical seo beyond page speed, architecture is the next big lever.
Best practices:
- Keep depth shallow: 3 clicks to key pages.
- Use clean, descriptive URLs: /category/subcategory/product
- Breadcrumbs with structured data (BreadcrumbList).
- Contextual links in body copy to related topics/products.
- Avoid infinite URL spaces (calendars, sort parameters, session IDs).
- Create hubs/pillars and link clusters to them.
Internal links help bots distribute crawl equity and understand topical relationships critical for large catalogs and content libraries.
Crawl Budget: Spend It on What Matters
Crawl budget = how many pages bots are willing and able to crawl. For massive sites, it’s a big deal.
Reduce waste:
- Block crawling of internal search results and faceted combinations you don’t want indexed via robots.txt.
- Use noindex for thin pages (but allow crawling if you want directives seen).
- Eliminate redirect chains and loops.
- Consolidate duplicate parameters and near-duplicates.
High-value pages should be easy to reach, linked in nav/footers/sitemaps, and return fast 200 responses.
Indexing Controls: Canonical, Noindex, Disallow (Know the Difference)
When learning what is technical seo, this trio trips up many teams. Here’s how they differ.
- Canonical: Suggests the preferred version among duplicates.
- Noindex: Tells search engines not to index a page (can still be crawled).
- Disallow (robots.txt): Blocks crawling; bots may still index the URL if discovered elsewhere, but without content.
Quick reference:
| Goal | Use | Notes |
| Consolidate duplicates | rel=”canonical” | Keep consistent internal links to canonical URL |
| Remove from index | meta robots noindex or x-robots-tag | Allow crawling so the directive is seen |
| Stop crawling low-value areas | robots.txt Disallow | Don’t use to remove indexed pages |
| Control link equity | nofollow (rarely needed sitewide) | Prefer strong IA and canonicalization |
Examples:
- Meta robots:
text
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex,follow” />
- HTTP header (x-robots-tag):
text
X-Robots-Tag: noindex, follow
Structured Data: Earn Rich Results (The Right Way)
Structured data helps machines understand your content. It’s central to what is technical seo for enhanced visibility.
Popular types:
- Organization, WebSite (with Sitelinks Search Box)
- Article/BlogPosting
- Product (with price, availability), Review
- FAQPage, HowTo, Event, JobPosting, LocalBusiness
JSON-LD example (Article):
text
<script type=”application/ld+json”>
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “Article”,
“headline”: “What Is Technical SEO & Why It’s Crucial”,
“author”: {“@type”: “Person”, “name”: “Your Name”},
“datePublished”: “2025-01-15”,
“image”: [“https://www.example.com/images/technical-seo-guide.jpg”],
“publisher”: {
“@type”: “Organization”,
“name”: “Your Brand”,
“logo”: {“@type”: “ImageObject”, “url”: “https://www.example.com/logo.png”}
}
}
</script>
Validate and monitor in GSC. Note: Eligibility doesn’t guarantee rich results. Docs: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/appearance/structured-data/intro-structured-data
JavaScript SEO: Render Without Roadblocks
Modern frameworks can delay or block content if not handled carefully.
Guidelines:
- Ensure primary content and links appear in the HTML source when possible.
- Defer non-critical JS; avoid blocking CSS/JS.
- Use server-side rendering (SSR) or pre-rendering for content-heavy templates.
- Don’t rely on client-side rendering for essential metadata, canonical tags, or links.
- Test with “View Page Source” vs. “Rendered HTML,” and the URL Inspection tool in GSC.
More: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/javascript
International SEO with Hreflang
For multilingual or multi-regional sites, hreflang prevents wrong-language rankings and duplicate confusion.
Rules:
- Use language-region codes (e.g., en-gb, en-us, es-es).
- Implement reciprocal and self-referencing tags.
- Prefer subfolders (example.com/uk/) or subdomains over parameter-only solutions.
Example:
text
<link rel=”alternate” href=”https://example.com/” hreflang=”en-us” />
<link rel=”alternate” href=”https://example.com/uk/” hreflang=”en-gb” />
<link rel=”alternate” href=”https://example.com/es/” hreflang=”es-es” />
<link rel=”alternate” href=”https://example.com/” hreflang=”x-default” />
Mobile-First Indexing and UX
Technical SEO today means the mobile version must be complete and fast.
Checklist:
- Responsive design with consistent primary content on mobile and desktop.
- Same structured data and meta tags on both.
- Tap targets large enough; lazy-load responsibly.
- Avoid intrusive interstitials that block content.
Security, HTTPS, and Reliability
Trust is part of what is technical seo. Search engines and users expect:
- HTTPS everywhere; redirect HTTP → HTTPS with 301s.
- HSTS for stricter security (server header Strict-Transport-Security).
- Fix mixed content and outdated TLS.
- Leverage CDN caching, edge security, and DDoS protection.
Redirects, Status Codes, and Site Moves
- 200 OK: Healthy page.
- 301 Moved Permanently: Use for canonicalization and site migrations.
- 302/307: Temporary; avoid for permanent moves.
- 404/410: Cleanly deprecate dead pages and update internal links.
- Avoid chains (e.g., A→B→C); aim for A→C direct.
Site move with URL changes: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/site-move-with-url-changes
E‑commerce Technical SEO Essentials
If you sell online, technical discipline avoids index bloat and cannibalization.
- Faceted navigation: Disallow crawl of endless combinations; canonicalize back to the clean category; use noindex for thin filter pages you need accessible.
- Variants: Consolidate with canonical and structured data for variant attributes (size, color). Keep one primary product URL.
- Out-of-stock: Keep page live with availability markup; avoid deleting high-authority product pages.
- Pagination: Use clear rel=“prev/next” for users and strong internal links; canonical to page-specific URLs (not page 1).
Local and Multi-Location Technical SEO
- Create unique, indexable location pages with Name, Address, Phone (NAP), hours, and embedded map.
- Use LocalBusiness structured data with geo coordinates.
- Keep NAP consistent across the site and directory listings.
- Optimize store finder pages for crawlability and speed.
Accessibility as Technical SEO
Accessible sites are often more crawlable and usable:
- Semantic HTML (headings, lists, landmarks).
- Alt attributes for meaningful images.
- Sufficient color contrast and focus states.
- Descriptive link text, not just “click here.”
This improves user satisfaction and can indirectly support rankings and conversions.
Measurement and Monitoring
- Google Search Console: Coverage, Sitemaps, Core Web Vitals, Enhancements, Manual Actions.
- PageSpeed Insights + Lighthouse: Field and lab data.
- Log file analysis: Understand bot behavior and crawl allocation.
- Analytics: Track conversions on canonical, indexable URLs; annotate changes.
- Dashboards: Monitor 404s, 5xx errors, CWV, indexable pages, and top templates weekly.
Common Technical SEO Mistakes (To Avoid Immediately)
- Blocking CSS/JS in robots.txt
- Accidentally noindexing critical templates
- Infinite URL spaces from filters/sort/search
- Duplicate content from parameters and trailing slash mismatches
- Wrong or self-contradictory canonical tags
- Redirect chains/loops and 302s used for permanent moves
- Uncompressed, oversized images hurting LCP
- Cumulative Layout Shift from ads or late-loaded fonts
- Missing or broken XML sitemaps
- Hreflang without reciprocity or wrong language-region codes
- Client-side rendering of essential content only
- Mixed content after HTTPS migration
- Orphaned pages not linked internally
- Thin or empty paginated states indexed
- Robots.txt used to remove indexed pages (use noindex)
- Massive JavaScript bundles blocking interaction (INP failures)
- Missing breadcrumbs and weak IA
- Structured data errors or spammy markup
- Staging environments indexable
- Ignoring server logs and real-user data
Helpful Tools and Docs
- Google Search Console: https://search.google.com/search-console
- PageSpeed Insights: https://pagespeed.web.dev/
- Web Vitals guidance: https://web.dev/vitals/
- JavaScript SEO: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/javascript
- Sitemaps: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/sitemaps/overview
- Canonicalization: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/consolidate-duplicate-urls
- Robots meta and x-robots: https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/robots-meta-tag
If you’d like these set up and benchmarked for you, we can help at https://ghodkes.com/.
Bonus: Quick Technical SEO Checklist
- Crawl the site and export issues (4xx/5xx, chains, duplicates)
- Validate index coverage in GSC and clean XML sitemaps
- Review robots.txt, meta robots, and x-robots-tag usage
- Set canonicals consistently; fix mixed canonical/internal linking
- Improve LCP, CLS, INP with targeted performance fixes
- Simplify navigation; add breadcrumbs and contextual links
- Control parameters and faceted navigation; prevent index bloat
- Implement and validate structured data (JSON-LD)
- Ensure mobile parity and fast mobile performance
- Secure with HTTPS, HSTS; fix mixed content; clean status codes
- Validate JavaScript rendering; consider SSR/pre-render for key templates
- Implement hreflang correctly for international sites
- Monitor logs, GSC, and dashboards; annotate changes
If you want expert hands on the wheel, we’re here to help: https://ghodkes.com/
Conclusion: Make Your Site Easy to Find, Fast to Load, and Simple to Trust
Now that you’ve seen what is technical seo from crawling and rendering to Core Web Vitals, canonical tags, hreflang, and structured data you’ve got a clear roadmap to unlock growth already hiding in your site. In 2025, the winners make pages effortless for both users and crawlers. Do that consistently, and rankings, traffic, and conversions follow.
Want Your Website to Rank Higher With a Perfect Technical SEO Setup?


Technical SEO is the foundation of every successful ranking strategy.
If your site is slow, unstructured, or difficult for Google to crawl…
you will NEVER rank no matter how good your content is.
At SparXcellence Ghodke’s LLP, we help businesses fix:
✔ Crawling & indexing issues
✔ Slow-loading pages
✔ Core Web Vitals errors
✔ Duplicate/Thin content
✔ Technical errors hurting rankings
✔ Sitemap, robots.txt, schema & more
Get a FREE Technical SEO Audit (Limited Slots)
We’ll scan your site and show you exactly what’s stopping you from ranking.
Book Your FREE Audit:
https://ghodkes.com/contact-us/
What is technical seo?
Technical SEO ensures search engines can crawl, render, and index your site effectively. It covers speed, Core Web Vitals, architecture, sitemaps, robots, canonical tags, structured data, mobile-first indexing, and more.
Why is technical SEO important in 2025?
Performance, reliability, and clarity are table stakes. Solid technical foundations improve discoverability, user experience, and conversions especially with mobile-first indexing and complex JS sites.
How do I check if my site has technical issues?
Start with a full crawl, review GSC coverage, validate sitemaps, and test Core Web Vitals. Then inspect canonical tags, robots directives, and internal linking. This is the practical way to learn what is technical seo hands-on.
What should be in a technical SEO audit?
Crawl diagnostics, index coverage, sitemaps, robots, Core Web Vitals, internal links, structured data, canonicalization, status codes, security, JavaScript rendering, and (if applicable) hreflang.
How do I improve Core Web Vitals?
Optimize hero images, compress and serve next-gen formats, reduce render-blocking resources, stabilize layouts, and trim heavy scripts. Target LCP ≤ 2.5s, CLS ≤ 0.1, INP ≤ 200 ms.




