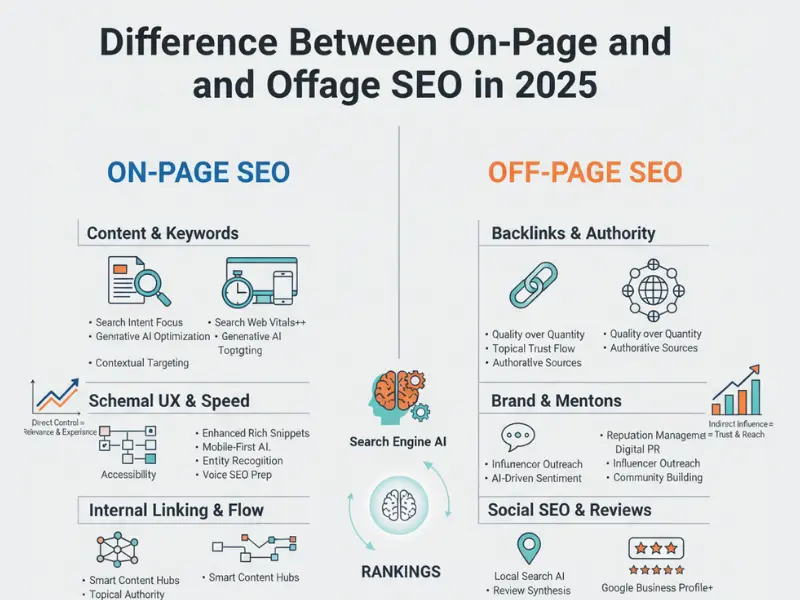
If you want more qualified traffic without constantly increasing ad spend, you’ve probably asked about the difference between on page and off page SEO. In 2025, the answer is a game‑changer: on‑page work makes your pages discoverable, understandable, and satisfying. Off‑page work proves to the wider web that you’re credible and worth ranking. Ignore either side and results plateau. Learn to combine them and performance compounds.
This guide cuts through jargon. You’ll get a plain‑English explanation of the difference between on page and off page SEO, what’s included in each, why both are vital in today’s search landscape, how to measure success, and common mistakes to avoid. We’ll share industry‑specific examples (local, ecommerce, B2B, publishers), up‑to‑date best practices, and FAQs you can send to teammates and clients.


TL;DR: The Difference at a Glance
- On‑page = what you control on your site: content, structure, internal links, speed, mobile UX, accessibility, structured data, and helpfulness.
- Off‑page = how the web responds to you: links, brand mentions, reviews, citations, partnerships, and signals that indicate authority and trust.
- The difference between on page and off page SEO boils down to control vs. influence. On‑page is your workshop. Off‑page is your reputation. You need both to win.
Why the Difference Between On‑Page and Off‑Page SEO Matters More in 2025
Three shifts make this especially important right now:
- Search overviews and rich features. Summary‑style answers and result enhancements favor pages that are structured, fast, and helpful (on‑page) and that are backed by credible sources (off‑page).
- Mobile behavior. Most local and commercial searches happen on phones. Poor speed or readability (on‑page) kills engagement, while strong reviews and local citations (off‑page) sway clicks.
- Trust‑first results. Signs of experience, expertise, and reputation think author bios, real photos, quotes, and third‑party mentions rise in value.
If you understand the difference between on page and off page SEO and plan for both, you’ll gain visibility where customers decide.
On‑Page SEO: What It Includes (and Why It Drives Conversions)


On‑page is everything you can directly change on your website to make it easy for people and search engines to understand and use.
Core Components of On‑Page SEO
Search Intent & Information Architecture
- Map each page to one primary intent (informational, commercial, transactional).
- Build a logical hierarchy: homepage → category/pillar → subcategory/cluster → detail pages.
- Make navigation clear and internal links descriptive.
Content Quality: People‑First, Search‑Smart
- Lead with the answer: a crisp summary at the top showing you understand the question.
- Use meaningful headings (H2/H3) and short paragraphs; add bullets for lists.
- Provide unique value: data, screenshots, case examples, step‑by‑step walkthroughs, local details.
On‑Page Elements
- Titles and meta descriptions that set accurate expectations and earn clicks.
- Structured data (FAQPage, HowTo, Product, Article, LocalBusiness, BreadcrumbList) to clarify meaning.
- Image optimization: descriptive file names, alt text, compression, and modern formats.
UX, Accessibility & Speed
- Core Web Vitals: quick loads, responsive interactions, stable layout.
- Accessible design: high contrast, keyboard navigation, alt text, readable font sizes.
- Mobile‑first: large tap targets, short forms, obvious calls to action.
Internal Links That Guide
- Link from related pages with natural, descriptive anchors.
- Build hub‑and‑spoke structures that concentrate authority and help users find the next step.
- Keep “orphan” pages (with no internal links) off your site.
Trust Signals on Page
- Real authorship and credentials; transparent policies (returns, privacy).
- Genuine reviews and testimonials (marked up with schema where allowed).
- Photos of real teams, work in progress, storefronts, and product details.
Where to focus first:
- Top revenue pages (service, category, product).
- Pages already receiving impressions but low CTR (improve titles/meta).
- Pages with high traffic but low conversions (clarify intent, strengthen CTAs, add FAQs).
Off‑Page SEO: What It Includes (and Why It Builds Authority)
Off‑page is everything that happens beyond your site to signal credibility and relevance.
Core Components of Off‑Page SEO
Links & Digital PR
- Earn editorial links from relevant sites: industry publications, associations, quality blogs, and local media.
- Create link‑worthy assets: data studies, checklists, comparison guides, calculators, before/after galleries.
- Pitch value: helpful resources for community partners, chambers, and nonprofits.
Brand Mentions & Co‑Citations
- Mentions without links still help search engines connect you to topics.
- Appear in “best of” lists, buying guides, and industry roundups.
- Collaborate with complementary brands for co‑authored content.
Reviews & Reputation
- Collect reviews on platforms that matter (Google Business Profile, industry sites).
- Reply to every review show empathy and specifics.
- Display review snippets on your site (with appropriate schema and platform rules).
Citations & Local Listings
- Ensure consistent name, address, and phone across major directories and niche listings.
- Fix duplicates and inaccuracies that create confusion.
Social Proof & Community
- Social engagement isn’t a direct ranking factor, but it drives brand searches and discovery.
- Events, sponsorships, scholarships, and community contributions often lead to high‑quality mentions.
Focus areas for off‑page vary by industry. Local services lean on citations and reviews; ecommerce leans on PR and creator coverage; B2B leans on expert mentions, webinars, associations, and case studies.
Side‑by‑Side: The Practical Difference Between On‑Page and Off‑Page SEO
| Dimension | On‑Page SEO | Off‑Page SEO |
| What it is | Control your site’s clarity, structure, and experience | Earn trust from other sites and platforms |
| Primary goal | Relevance, usefulness, engagement, conversions | Authority, credibility, popularity |
| Speed to impact | Weeks (title/meta fixes, UX upgrades) | Weeks–months (outreach, mentions, reviews) |
| Level of control | High (you own it) | Medium–low (you influence, others decide) |
| Main KPIs | Impressions, CTR, dwell time, conversions | Referring domains, review velocity, brand searches |
| Risks | Thin/duplicate content, poor UX, slow pages | Low‑quality links, spam tactics, review gating |
| 2025 significance | Needed for rich results and overviews | Needed to be cited and trusted |
This table captures the real difference between on page and off page seo: relevance vs reputation. You need both to rank and convert.
How They Work Together (Synergy That Compounds)
- Internal links pass authority to pages that can convert and satisfy users (on‑page helps off‑page value flow).
- Structured, helpful pages are easier for publications to reference (on‑page attracts better links).
- Reviews lift map pack rankings and improve click‑through to well‑optimized location pages (off‑page feeds on‑page).
- A positive reputation increases brand searches. On‑page excellence turns those brand clicks into revenue.
If you’re asking about the difference between on page and off page SEO to prioritize work, start on‑page for quick wins and conversion improvements, then layer off‑page to keep momentum.
Industry‑Specific Examples
Local Services (plumbers, dentists, clinics, home services)
- On‑page: service pages with clear pricing ranges, process steps, emergency instructions, and location pages with parking/transit tips.
- Off‑page: reviews, citations, association links, community press.
- Outcome: show up in map pack and organic, then convert with clarity and trust.
Ecommerce & DTC
- On‑page: category copy that answers buyer questions, product schema, fast images, FAQs on PDPs, comparison tables.
- Off‑page: digital PR (launches, “how we build it”), creator coverage, “best of” lists.
- Outcome: rank for commercial queries, earn featured mentions, and reduce ad dependence.
B2B & SaaS
- On‑page: pillar pages for core problems, implementation playbooks with screenshots, ROI calculators, real case stories.
- Off‑page: expert quotes, industry associations, webinars, co‑authored content, selective directory listings.
- Outcome: rank for problem‑to‑solution queries; authority lifts competitive terms.
Publishers & Content Sites
- On‑page: tight intros, helpful tables, step‑by‑steps, schema; keep evergreen content fresh.
- Off‑page: reputable citations, ethical syndication, expert contributors.
- Outcome: be the source overviews and roundups cite.
Measurement: KPIs That Show If It’s Working
On‑Page KPIs
- Impressions and ranking distribution (Top 3/10/50) by topic
- CTR by query and page (title/meta improvements)
- Engagement: scroll depth, time on page, bounce rate (interpret carefully)
- Conversions: calls, forms, bookings, cart adds, purchases
- Index coverage and Core Web Vitals pass rates
Off‑Page KPIs
- Referring domains and link quality (contextual, relevant, editorial)
- Review count, recency, average rating, response rate
- Citations: coverage and consistency
- Brand mentions and branded search trendlines
Combine both views to judge the effectiveness of your strategy.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
On‑Page Mistakes
- Keyword stuffing and thin content. Fix by writing for people first: answer questions, show steps, add proof.
- Ignoring mobile speed and UX. Fix by compressing images, simplifying pages, and testing on real devices.
- Unclear page purpose. Fix with a one‑topic‑per‑page rule and descriptive headings.
Off‑Page Mistakes
- Buying links or using private networks. Risky, short‑lived gains. Earn genuine mentions.
- Review gating (asking only happy customers). Violates platform policies and erodes trust. Ask everyone and reply to all.
- Chasing domain metrics over relevance. Seek links your audience actually uses.
The safest strategy is also the most durable: helpful pages and genuine reputation building.
2025 Best Practices to Win the Click (and the Customer)
On‑Page Enhancements
- Lead with a summary that answers the main question.
- Add a table of contents to long pages with jump links.
- Use comparison tables and “what to know before you buy/visit.”
- Insert real photos and short clips that show people and process.
- Mark up FAQs and product/service details with appropriate schema.
- Improve Core Web Vitals especially on mobile.
Off‑Page Enhancements
- Develop one link‑worthy asset each quarter (data study, guide, tool, case gallery).
- Join associations and contribute helpful content to their sites.
- Launch a review request habit with a short link or QR code at point of service.
- Fix citations and maintain them as information changes.
- Pitch community stories the press actually wants.
These habits strengthen both sides of the equation.
Real‑World Signals of E‑E‑A‑T (That You Can Control)
- Show who wrote the page and why they’re qualified.
- Include “how we tested,” “what we measured,” or “what we’d do differently next time.”
- Link to reputable sources where appropriate transparency builds trust.
- Keep content updated (note “last updated” with meaningful changes).
- Make contact options obvious and policies clear.
These signals help search engines and humans choose you.
The Most Useful Tools (Keep It Lean)
- Search Console: queries, CTR, coverage
- Analytics: conversions, paths, top pages
- Crawlers (Screaming Frog/Sitebulb): on‑page health and internal links
- PageSpeed Insights/Lighthouse: performance and Core Web Vitals
- Local tools: GBP manager, review aggregator, citation tracker
- PR monitoring: alerts for mentions; keep a press page updated
Tools don’t win process and consistency do. Use a lean stack you’ll actually maintain.


Conclusion: Put Both Hands on the Wheel
The difference between on page and off page SEO isn’t academic it’s the roadmap to durable growth. On‑page gets you in the race and turns visitors into customers. Off‑page earns the nod from the wider web that pushes you to the front. When you combine both clear, helpful pages and genuine reputation building you create a compounding engine that outlasts algorithm swings and ad auctions.
Where to act first:
- Improve titles/meta on your top revenue pages; add a clear summary, FAQs, and internal links.
- Strengthen mobile speed and accessibility.
- Launch a steady review and response habit; fix your citations.
- Develop one link‑worthy asset this quarter and pitch it to relevant sites.
That’s how you put the difference between on page and off page SEO to work so search doesn’t just send traffic, it sends customers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the core difference between on page and off page SEO?
On‑page focuses on your site’s content, structure, and experience everything you control. Off‑page focuses on signals from other sites and platforms links, mentions, reviews, and citations. In short, relevance vs reputation. The difference between on page and off page SEO is why you need both to rank and convert.
Which should I prioritize first on‑page or off‑page?
Start with on‑page to fix clarity, speed, and conversion on your most valuable pages. Then invest in off‑page to earn citations and reviews that lift competitive rankings. The compounding effect comes from doing both.
How does site speed affect the difference between on page and off page SEO?
Speed is an on‑page factor that impacts user satisfaction and eligibility for certain features. Faster pages engage visitors longer, which makes off‑page efforts more effective because visitors who arrive from links stay and act.
What are examples of off‑page SEO beyond links?
Reviews and replies, business citations, local press, association listings, co‑authored content, and unlinked brand mentions. These signals help confirm authority and trust.
How can I tell if I’m over‑optimizing?
If your copy reads unnaturally or repeats phrases awkwardly, you’re over‑optimizing. Write for clarity; use synonyms; cover related questions; avoid stuffing. The difference between on page and off page SEO is not “keywords vs links” it’s “helpfulness vs reputation.”
Do social signals count as off‑page SEO?
Social activity isn’t a direct ranking factor, but it drives brand searches, discovery, and links/mentions. It supports off‑page success indirectly.
How do I measure the impact of my off‑page work?
Track referring domains (quality and context), review volume/recency, branded search growth, and incremental improvements to rankings and CTR on pages you’re promoting.
What changes in 2025?
Richer search features and overview panels reward helpful structure and trusted sources. On‑page must be clear, fast, and accessible; off‑page must be genuine and relevant.